A pituitary macroadenoma is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that arises from the pituitary gland. The term "macroadenoma" refers to the size of the tumor, which is larger than 1 centimeter in diameter. The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain and regulates various hormonal functions, so a macroadenoma can disrupt hormone production and pressure surrounding brain structures.
Signs and Symptoms:
Hormonal imbalances: Excess or deficiency of hormones such as growth hormone, cortisol, thyroid hormones, and sex hormones.
Prolactinoma: Excess prolactin causes irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, and galactorrhea (milk production) in women; reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, and infertility in men.
Acromegaly: Excess growth hormone causing enlarged hands, feet, facial bones, and thickened skin.
Cushing’s syndrome: Excess cortisol causes weight gain, thinning skin, high blood pressure, and muscle weakness.
Pressure effects: Due to the size of the tumor, symptoms can result from compression of nearby structures.
Headaches: Common due to pressure on surrounding tissues.
Vision problems: Blurred or double vision, or loss of peripheral vision (bitemporal hemianopia), due to optic chiasm compression.
Fatigue, weakness, or dizziness: Resulting from hormone deficiencies or pressure on the brain.
Nausea or vomiting: Due to increased intracranial pressure.
Treatment Approaches :
1. Allopathic (Conventional Medicine) :
Medications: Dopamine agonists (e.g., bromocriptine, cabergoline) are used for prolactinomas to reduce prolactin production and shrink the tumor. Somatostatin analogs (e.g., octreotide) control growth hormone in acromegaly. Corticosteroid inhibitors in cases of Cushing's syndrome.
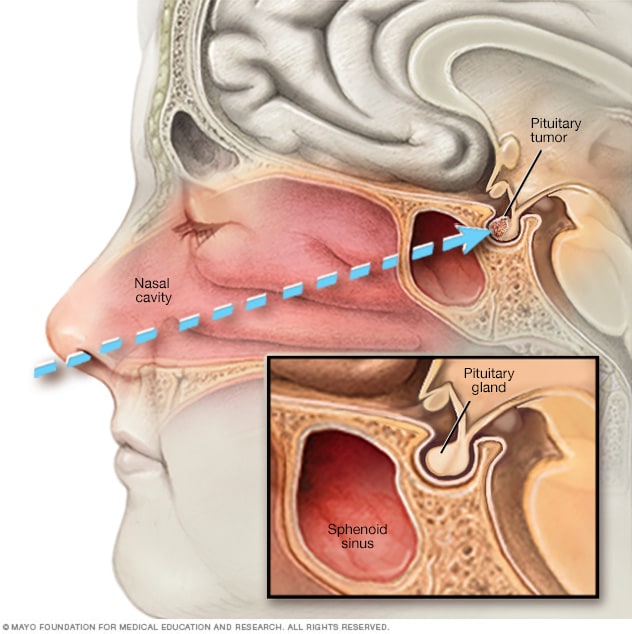
Surgery: The primary treatment for non-prolactin-secreting tumors and large macroadenomas is transsphenoidal surgery, where the cancer is removed through the nasal cavity.
Radiotherapy: Used when surgery is not completely effective or feasible, or when the tumor recurs.
Hormone replacement therapy: For deficiencies caused by the tumor or its treatment (e.g., thyroid, cortisol, or sex hormone replacements).
2. Homeopathic Treatment :
Homeopathic remedies are individualized based on the patient’s symptoms, constitution, and overall health.
Some common remedies used for pituitary-related disorders include:
Calcarea carbonica: Often used for patients with slow metabolism, fatigue, and weight gain.
Lycopodium: For digestive issues, weakness, and mental fatigue.
Phosphorus: For nervous exhaustion, fatigue, and emotional sensitivity.
Sepia: Often used in cases involving hormonal imbalances, especially in women with menstrual issues or infertility.
Pituitrinum: A specific remedy for pituitary-related dysfunctions.
Goal of treatment: Focuses on balancing the endocrine system, reducing tumor size, and addressing individual symptoms (headaches, vision problems, etc.).
3. Ayurvedic Treatment :
Ayurvedic treatment focuses on balancing the body’s doshas (vata, pitta, and kapha) and improving overall hormonal function.
Herbal remedies:
Ashwagandha: Adaptogen that helps in balancing hormones, reducing stress, and improving strength.
Shatavari: Known for its hormone-balancing properties, particularly in women.
Brahmi: Used to improve cognitive function and reduce stress.
Triphala: Helps in detoxification and improving digestive health.
Guggul: For reducing inflammation and balancing thyroid function.
Panchakarma therapy: Detoxification treatments to purify the body and restore balance.
Diet and lifestyle modifications: Emphasis on a balanced diet, stress reduction techniques (such as yoga and meditation), and regular physical activity to improve overall vitality and manage symptoms.
Each system of treatment offers different approaches, and patients may opt for one or a combination of treatments depending on their specific conditions and preferences. Individuals need to consult their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan.
A pituitary macroadenoma is a noncancerous tumor that arises from the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland is a vital part of the endocrine system, responsible for producing hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction. A macroadenoma is classified as a tumor that is larger than 1 centimeter in diameter. These tumors can affect hormone production and cause pressure on nearby structures, such as the optic nerves, leading to various symptoms.
Signs and Symptoms of Pituitary Macroadenoma:
1. Hormonal Imbalance:
Hypersecretion: The tumor may produce excess hormones, leading to conditions like:
Cushing's disease (excess cortisol): Weight gain, high blood pressure, bruising, and muscle weakness.
Acromegaly (excess growth hormone): Enlarged hands, feet, facial features, and joint pain.
Hyperprolactinemia (excess prolactin): Irregular menstrual periods in women, erectile dysfunction in men, and breast milk production (galactorrhea).
Hyposecretion: The tumor may reduce hormone production, leading to:
Fatigue, weakness, weight loss, and low blood pressure. Reduced libido and fertility issues.
2. Pressure Symptoms:
Headaches: Tumors can cause headaches due to increased pressure within the skull.
Vision problems: The tumor may compress the optic nerves, leading to blurry vision, double vision, or loss of peripheral vision (bitemporal hemianopia).
Nausea and vomiting: Increased pressure on the brain may also cause these symptoms.
3. Other Possible Symptoms:
Cognitive and mood changes. Difficulty in balancing and coordination. Decreased sexual function (erectile dysfunction in men, loss of libido in both genders).
Conventional Treatment of Pituitary Macroadenoma:
1. Medications:
Dopamine agonists (e.g., cabergoline, bromocriptine) to shrink prolactinomas. Somatostatin analogs (e.g., octreotide, lanreotide) and growth hormone receptor antagonists for growth hormone-secreting tumors. Steroid therapy for adrenal insufficiency or other hormonal replacement as needed.
2. Surgery: Transsphenoidal surgery is commonly used to remove the tumor. It involves accessing the tumor through the nasal passage.
3. Radiation Therapy: Used if surgery is not completely effective or feasible.
4. Hormone Replacement Therapy: If the pituitary gland’s hormone production is affected, lifelong hormone replacement may be necessary.
Homeopathic Treatment for Pituitary Macroadenoma:
Homeopathic treatment is based on the individual’s unique symptom profile and aims to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes. Homeopathy looks at both physical and psychological symptoms and tailors treatment to the patient's overall constitution. Below are some key remedies that may be considered based on specific symptoms, though individualized treatment by a professional homeopath is essential.
1. Calcarea Carbonica: Suitable for patients with symptoms of obesity, fatigue, and cold intolerance.
Commonly prescribed when there is a sense of pressure in the head, along with sensitivity to cold and stress. Can help in managing symptoms related to hypothyroidism or adrenal insufficiency caused by hormonal imbalances.
2. Lachesis: Often used in cases of congestion, especially with circulatory issues and headaches. Can help in cases where there is intense pressure in the head, especially with vision issues such as blurred vision or visual field defects.
3. Sepia: Often prescribed for women experiencing hormonal imbalances, particularly prolactin or estrogen-related issues. Useful in cases of irregular periods, emotional disturbances, or low energy and libido.
4. Phosphorus: Can help with symptoms like headaches, vision problems, and exhaustion. Often given to patients with significant nervous system involvement, particularly those who are prone to nervousness, anxiety, or emotional distress.
5. Belladonna: For acute headache episodes or visual disturbances associated with macroadenomas. The patient may experience sharp pains, redness in the face, and sensitivity to light.
6. Pituitarum: A remedy that is often indicated for issues related to pituitary function. It can be used in cases where there is a significant hormonal imbalance, including symptoms related to both hyperfunction and hypofunction of the gland.
Holistic Approach in Homeopathy: Homeopathic treatment for pituitary macroadenoma requires a holistic understanding of the patient. The treatment will typically involve:
Case-taking: A thorough evaluation of not just the physical symptoms, but also emotional, mental, and behavioral traits.
Individualized Prescription: Unlike conventional medicine, there is no one-size-fits-all remedy. The treatment is individualized to suit the person’s constitution.
Long-term Care: Pituitary macroadenomas are slow-growing tumors. Regular follow-ups with the homeopath are important, and in some cases, homeopathic treatment may work alongside conventional methods for symptom relief and healing.
Lifestyle and Supportive Measures:
In addition to homeopathic remedies, lifestyle changes and supportive care may be necessary:
Diet and Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is important to support overall health and recovery.
Regular Monitoring: For those with macroadenomas, regular check-ups with an endocrinologist or neurologist are crucial to monitor the size and activity of the tumor.
Conclusion: Homeopathy offers a natural and gentle approach to managing the symptoms of pituitary macroadenoma by focusing on the individual's overall health and well-being. However, due to the complexity of the condition and its potential risks (especially concerning vision and hormone regulation), homeopathic treatment must be considered as a complementary option alongside conventional medical care.
Kazi shaif uddin ahmed.
>Share by:


Make a comments as guest/by name or from your facebook:
Make a comment by facebook: